Observing Beyond our Senses – Career Connections Summarized
 see.isbscience.org/observing-beyond-our-senses/career-connections-summarized/
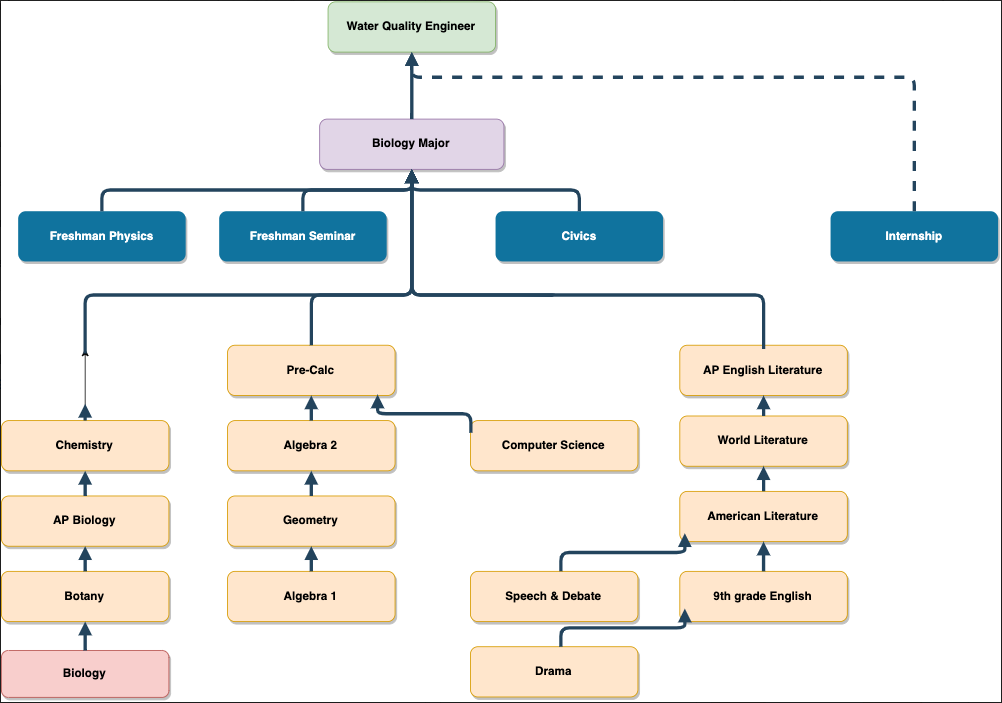
see.isbscience.org/observing-beyond-our-senses/career-connections-summarized/Within each OBOS lesson, there are outlines of career-connected activities that can be incorporated into the lesson. These can be located in the Career Connection Tab within each lesson page. In the table below, you will find a compiled list of options for teaching all of the career connected activities for the entire module. For each lesson, we have identified 4 options - choose an activity based on the time you have available. Feel free to modify activities based on your class's needs. You can also mix and match options. For instance, you can complete the option in Column A for Lesson 1 and then Column D for Lesson 3. Based on which options you choose, these career connections could add ~30 minutes of classtime to the OBOS module overall or as many as 6 additional class periods.
Within this module, we've identified four Systems Thinkers in STEM videos which are particularly relevant to OBOS:
Chris: invention, hardware, and engineering
Dana: open pancreas, communications, sensing and using proxy variables
Monish: data organization and interpretation
Amy: geology and geography education and communication
We made the Systems Thinkers in STEM videos to provide a platform for discussion and reflection. There's a infinite number of ways to structure classroom discussion and build skills. The options below are a few ways that have worked for us.
OBOS Lessons |
Parallel Career Connection Activity Options |
||||||||
LESSON 1 – INTRODUCTION TO SALINE ENVIRONMENTS & MICROBIAL HALOPHILESEnvironments of differing salinities form on earth. Human activities impact saline environments by altering the salinity and/or introducing pollution. Extremophilic organisms such as Halobacterium salinarum can live in high salinity environments. |
Additional Information: Example Careers: Extremophile Biologist, Hydrologist, Mining Engineer, National Park Director, Botanist, Heavy Equipment Operator, Local Historian Example Majors: Ecological Restoration, Biology, Chemistry, Engineering, Environmental Resource Management, Marine Biology Interview Tips: StoryCorps has an excellent 3 minute video on how to conduct an interview. Time-based education flowchart example:
This flowchart, made with the free online tool: www.draw.io, has an emphasis in the topics: MATH, SCIENCE, COMPUTER SCIENCE, HUMANITIES. Other topics can include: ART, MUSIC, DRAMA, HISTORY, etc. |
||||||||
LESSON 2 – DESIGN PROCESS-MEASURING WIND SPEEDThis introductory activity has students quickly cycle through a complete design procedure centered on a measuring challenge. Specific aspects of a design procedure, such as defining criteria or evaluating trade-offs, will be practiced again in later instrumentation activities. |
Additional Information: Example interview questions for Chris: You started with an interest in mechanical engineering, what made you want to combine fields and also study molecular biology? What was your process for coming up with new ideas to for solving complex problems? |
||||||||
LESSON 3 – INFERENCES FROM PROXY VARIABLES-MOCK AFMObservation is the skill of recognizing and noting some fact or occurrence in the natural world. Observation includes the act of measuring. To infer is to arrive at a decision or logical conclusion by reasoning from evidence. Scientists use observations to make inferences. |
Additional Information: Example interview questions for Dana: What skills did you already have when you started this project? How did you develop the other skills that you did not acquire through the communications major? |
||||||||
LESSON 4 – SIGNAL AND NOISEIn this set of activities, students will attempt to communicate using hand signals or assemble an operational amplifier to play their iPods through a small speaker. The focus of activities will be the concepts of signal and noise and the trade-offs involved in amplifying the signal. |
Additional Information: Example questions for Monish: What are some similarities you found between the skills needed for a pharmacy career path and a computer science career path? What advice do you have for someone to learn computer science if they do not have a computer science background? |
||||||||
LESSON 5 – INFERRING PROPERTIES AND CALIBRATIONThis lesson serves as the conceptual underpinning for understanding how light behavior can be used to measure concentrations with a spectrophotometer. Students should frame their observations around “particles” of light interacting with material in three observable ways: that light can pass through, bounce off, or be taken in by materials. |
Additional Information: Potential Careers of the guest speaker: -Hydrologist -Geologist -State or local government environmental regulator -Environmentally-oriented lawyer or litigator |
||||||||
LESSON 6 – DEATH VALLEY MIDDLE BASIN CASE STUDYMeasurements of indicator species can be used to make inferences about environmental conditions. Quantity and resolution of a data collection plan is limited by resources. Mine tailings are point sources of heavy metal pollution. |
Additional Information: If you are having students present an elevator speech, you might consider having students interview one another in some round robin situations, to get and give feedback and what they’re considering including in the speech.
|